memcached is a general-purpose distributed memory caching system
originally developed by Danga Interactive for LiveJournal but now used
by many other sites. It is often used to speed up dynamic
database-driven websites by caching data and objects in RAM to reduce
the number of times an external data source (such as a database or API)
must be read. Here we describe the options available from the command
line to control a memcached instance via unix socket or IP:port.
Memcached can be set up to either take control commands via an IP address and port or via a unix socket.
Starting up
When listening via IP:port by default memcached listens for connections
on port 11211 and accepts connections from INADDR_ANY. To prevent
possibly malicious access you may want to consider restricting
connections to an internal or firewalled connection. Alternatively you
can set memcached to only listen for connections on localhost - i.e.
the server running the instance of memcached using 127.0.0.1.
To start up an instance of memcached listening on localhost port
11211 only use the following:
::sh
memcached -d -m memory -l 127.0.0.1
memoryis the maximum number of megabytes of memory you want memcached to use.If you want to specify a different port to listen on use the
-p PORToption.
Alternatively you can use unix sockets to communicate directly with the memcached instance. In this case commands can only be sent from a login shell that has access to the socket file - for example if you ssh into the server hosting it.
To start up memcached using unix sockets you would use the following command:
::sh
memcached -d -m memory -s ~/memcached.sock
This will create a file named memcached.sock in your home directory to
communicate through.
Memcache management
Memcached comes with a number of useful management commands.
Of these the most frequently useful are flush_all and the stats commands
including stats, stats items and stats slabs.
To send a command to memcached you can use nc (netcat). The general
form for all commands is:
echo "command" | nc 127.0.0.1 11211
Or for socket connections:
echo "command" | nc -U ~/memcached.sock
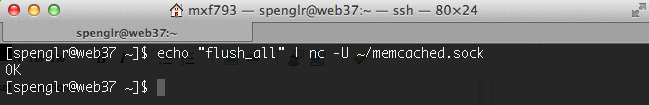
To flush the entire contents of your memcached instance you could issue
the flush_all command with one of the following:
echo "flush_all" | nc 127.0.0.1 11211 echo "flush_all" | nc -U ~/memcached.sock
Results in:
[user@web37 ~]$ echo "flush_all" | nc -U ~/memcached.sock OK
[user@web37 ~]$
To support developers in [[ countryRegion ]] I give a [[ localizedDiscount[couponCode] ]]% discount on all books and courses.
[[ activeDiscount.description ]] I'm giving a [[ activeDiscount.discount ]]% discount on all books and courses.
Statistics and state
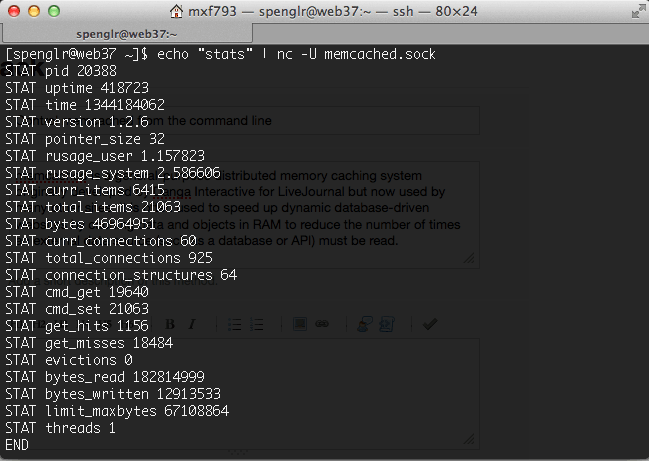
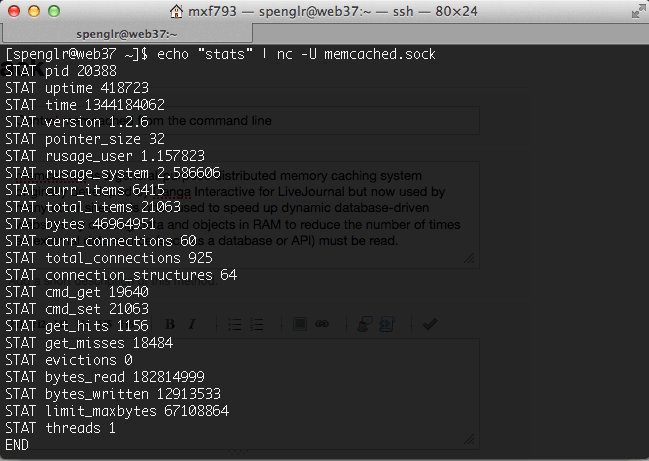
You can use the stats commands to get information about the state of your memcached instance. For example:
echo "stats" | nc 127.0.0.1 11211 echo "stats" | nc -U ~/memcached.sock
Will output a list of stats for the current instance. Additional
information can be found using stats items to give total stats about
items stored in the cached and stats slabs which provides more
information including performance hints.